How to Support Fine Motor Skills: Enhancing Dexterity and Precision in Everyday Life
Fine motor skills are essential for performing intricate tasks that require precision and control of small muscle groups. From buttoning a shirt to writing a letter, these skills play a crucial role in our daily lives. In this article, we will delve into the significance of fine motor skills, explore various activities to develop them, discuss supportive tools, and provide valuable insights for parents and caregivers.
Understanding Fine Motor Skills
Fine motor skills involve the coordination between the brain, muscles, and nerves to perform delicate movements. These skills are categorized into two main groups: gross manipulation and precise manipulation. Gross manipulation refers to activities involving larger muscles, like those used in crawling or gripping objects, while precise manipulation involves intricate movements like picking up a small object with thumb and finger.
Importance of Developing Fine Motor Skills
Fine motor skills are pivotal for both children and adults. In children, these skills contribute to academic readiness, handwriting proficiency, and cognitive development. For adults, well-developed fine motor skills enhance productivity in tasks such as typing, cooking, and artistic endeavors.
Factors Affecting Fine Motor Skill Development
Several factors influence the development of fine motor skills, including genetics, sensory processing, and early childhood experiences. Children who engage in activities that promote hand-eye coordination and finger strength tend to have more refined skills.
Activities to Enhance Fine Motor Skills
Playdough Creations: Squeezing and Shaping
Playing with playdough allows children to squeeze, roll, and shape, which strengthens hand muscles and fosters creativity.
Building with Blocks: Precision and Balance
Stacking blocks requires steadiness and balance, improving hand-eye coordination and spatial awareness.
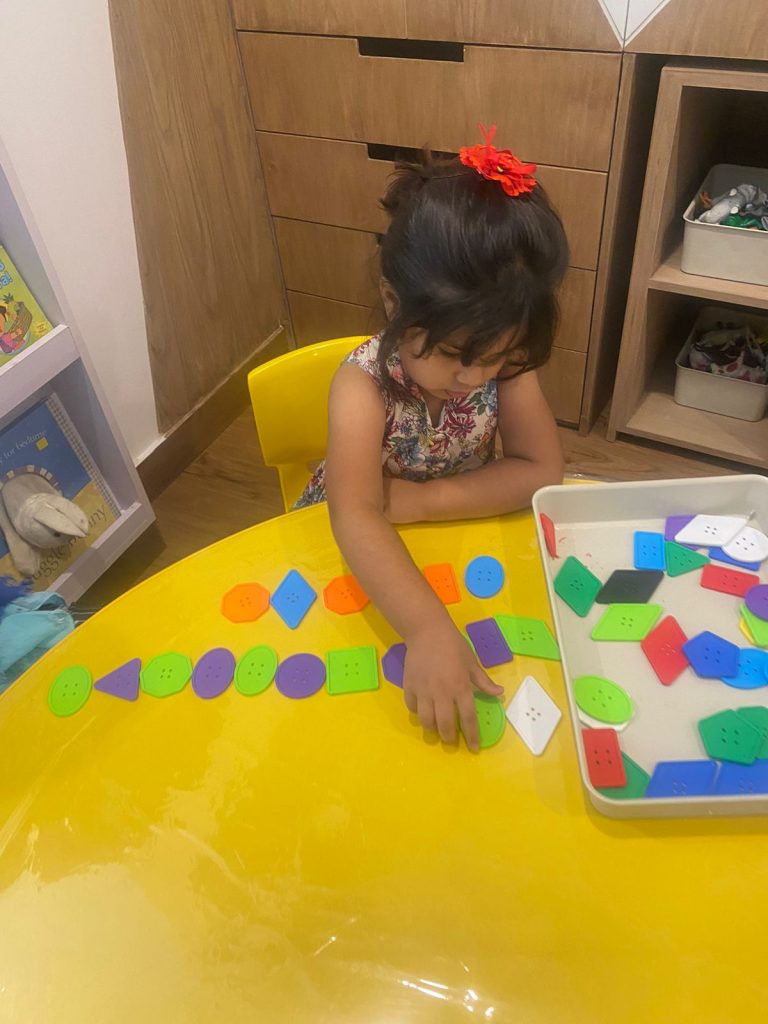
Puzzles and Manipulative Games: Problem-Solving and Coordination
Solving puzzles or working with manipulative games refines hand movements, spatial organization, and cognitive skills.
Drawing and Coloring: Hand-Eye Coordination
Drawing and coloring activities bolster fine motor skills while encouraging artistic expression.
Using Tongs and Tweezers: Grasping and Control
Picking up small objects using tongs or tweezers hones precision and control over hand movements.
Incorporating Fine Motor Activities into Daily Routine
Mealtime Tasks: Utensil Use and Self-Feeding
Encourage children to use utensils for self-feeding, aiding in the development of finger strength and grip control.
Dressing and Fastening: Buttons, Zippers, and Laces
Getting dressed independently refines fine motor skills as children learn to manipulate buttons, zippers, and laces.
Toothbrushing and Self-Care: Coordination and Independence
Engaging in self-care routines like brushing teeth enhances hand dexterity and fosters independence.
Supportive Tools and Toys for Fine Motor Skills
Play-Doh and Clay: Texture Exploration
These tactile materials encourage sensory exploration and strengthen hand muscles.
Building Toys and Manipulatives: Cognitive Engagement
Toys like building blocks enhance cognitive skills along with fine motor development.
Pencil Grips and Scissors with Spring Action: Writing Readiness
Pencil grips and modified scissors prepare children for handwriting by improving grip and control.
Pegboards and Beads: Precision and Planning
Creating designs with pegboards and beads refines hand coordination and planning abilities.
Fine Motor Skills and Academic Performance
Developed fine motor skills positively correlate with improved handwriting, spelling, and overall academic performance in school-aged children.
Addressing Fine Motor Challenges
If a child faces difficulties with fine motor skills, early intervention through occupational therapy and targeted activities can make a significant difference.
Tips for Parents and Caregivers
- Engage in Play: Participate in hands-on activities to support and model fine motor skills.
- Create a Stimulating Environment: Provide toys and tools that encourage exploration and manipulation.
- Be Patient: Mastery takes time; celebrate small achievements and progress.
- Incorporate Routine Activities: Embed fine motor activities into daily routines for consistent practice.
- Offer Varied Experiences: Introduce diverse activities to promote all aspects of fine motor skill development.
Developing fine motor skills is a journey that starts in early childhood and continues throughout life. These skills have far-reaching implications, influencing academic success, daily functionality, and overall quality of life. By incorporating engaging activities and being mindful of developmental milestones, parents and caregivers can provide valuable support to enhance fine motor skills in their children.